The affinity of FGAs for dopamine D2 receptors leads to EPS. These agents bind more tightly than dopamine itself to the D2 receptors while SGAs bind less avidly than dopamine to D2 receptors and allow normal dopamine transmission. The reduced blockade of D2 receptors has also been linked to antagonism of 5-HT2A serotonin receptors. Serotonin regulates dopamine release and the presence of serotonin in nigrostriatal dopamine pathway inhibits the release of dopamine, subsequently reversing some of D2 blockade by SGAs. Antipsychotic agents within the SGA class vary in their affinity to D2 receptors and risperidone has the highest affinity. Nevertheless, risperidone has been widely prescribed, particularly to elderly patients, with the expectation of a lower incidence of EPS compared to FGA treatment. In this study such lower risk of movement disorders has been confirmed up to approximately a year of therapy; however, a trend toward a weaker association was observed and the 95%CI of the adjusted HR at 360 days suggested a loss of statistical significance. The interpretation of these results needs to consider the limitations of observational studies based on administrative data. However, a number of steps were taken to account for potential confounding. The key covariates that are associated with outcome or exposure were identified and adjustments were made in the analysis. Age, sex, residence in a PCH and comorbidities were used to control for a possible selection bias. The index year was included into the adjusted models to account for possible changes in medical practice over the time frame of this study. The time frame of the study cohort did not include the time period of 1998 to 2000 when much of the shift between FGA and SGA use happened. No attempt was made to evaluate the effect of dose on incidence of EPS in this population, as small dose adjustments that commonly and continuously occur in clinical practise are not accurately captured by an observational study design that utilizes exclusively administrative data. Nevertheless, it is well known that EPS are dose-related and high doses of risperidone are expected to cause movement effects similar to those caused by FGAs. Furthermore, this study did not address the benefits of using antipsychotic pharmacotherapy, especially because quality of life cannot be assessed in observational studies that are based on administrative data. Yet the findings of this research provide a real-world observation that the use of risperidone is associated with lower risk for dyslipidemia was adjusted for major systemic parameters including socioeconomic factors potentially debilitating EPS adverse events in elderly subjects compared to the traditional antipsychotic medications. The advantage of this study is the fact that the entire elderly population of a Canadian province was included without restrictions due to insurance coverage or limited access. The results can be generalizable to other populations as they are not affected by sampling errors or recall bias.
Month: March 2019
Only one trial described the high dose chemoradiotherapy such as thalidomide
Hence, the aim of treatment for MM is to induce and maintain remission for as long as possible, thereby increasing the length of survival. Care of patients with MM is complex and focuses on treating the disease process and associated complications. A number of therapeutic approaches and treatment combinations have been employed in the treatment of MM, relying primarily on high dose chemotherapy and autologous stem-cell transplantation, maintenance therapy using drug regimens such as alternate-day prednisone. However, with these approaches, the response rates and survival times did not differ between patients designated as either high or low-risk according to M protein values and the symptoms or presence of bone disease; and early treatment did not benefit asymptomatic subjects nor did delayed treatment improve treatment efficacy and survival. The increased ability to precisely identify prognostic factors such as cytogenic abnormalities and to determine risk has increased the individualization of treatment for MM, improving patient response and survival. The incorporation of immunomodulators and proteasome inhibitors such as bortezomib into treatment regimens has improved the survival of patients with MM. Treatment with thalidomide, however, is often associated with toxicity that limits its long-term use. Single-agent clinical activity of these newer drugs has been limited and most patients still relapse, so the search continues for more effective combinations of drugs or drugs with new mechanisms of action. In 2011, the multiple myeloma guidelines of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network introduced several combinations of drugs for primary induction therapy: 1) the combination of bortezomib/cyclophosphamide/dexamethasone for transplant candidates; 2) the combination of bortezomib/dexamethasone for patients who are not Luciferase does not undergo the significant post-translational modification within the ER that envelope glycoproteins candidates for transplantation; and the combination of melphalan/prednisone/lenalidomide for nontransplant candidates. Lenalidomide, an analogue of thalidomide, appears to be equally efficacious and less toxic than thalidomide. Lenalidomide differs from thalidomide by a single carbonyl ring and an amino acid group. Mechanistically, lenalidomide inhibits proliferation of tumor cells and induces apoptosis, as well as exerting immunomodulator effects, notably stimulating the production of cytokines and the activation of T cells and natural killer cells. Lenalidomide also has anti-angiogenic properties and is a particularly attractive option for maintenance treatment of MM. Indeed, a number of comprehensive review studies have reported positive findings regarding the use of lenalidomide in the treatment of MM in recent years. 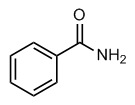 To gain a better, more complete understanding of the efficacy and safety of lenalidomide, we performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in which patients with MM received lenalidomide as initial or maintenance therapy. The methodological quality of the trials included in the metaanalysis is summarized in Table 2. Two trials reported acceptable methods of randomization.
To gain a better, more complete understanding of the efficacy and safety of lenalidomide, we performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in which patients with MM received lenalidomide as initial or maintenance therapy. The methodological quality of the trials included in the metaanalysis is summarized in Table 2. Two trials reported acceptable methods of randomization.
Further comprehensive research on the relationship between HE4 and Lewis should provide feasible theories
The functional and structural abnormalities of the ACC in FGIDs have been widely investigated. Similar to the insula, the activation of the ACC was commonly seen in neuroimaging studies on FGIDs. Our previous PET-CT study indicated that cerebral glycometabolism of the ACC in FD patients was significantly higher than that in the HS, and that the abnormal hyperactivity of the ACC was associated with symptoms and QOL of patients. Furthermore, some neuroimaging studies on IBS patients found a cortical thinning and a GMD increase in the ACC. In this study, we found that regional GMD in the bilateral ACC of the meal-related FD patient significantly decreased compared to the HS, and that the GMD decrease in the ACC was negatively correlated with the scores of symptoms and disease duration respectively. However, after correcting for depression and anxiety, the peak of GMC decrease within the ACC did not survive. Our result are consistent with Seminowicz DA’ s findings. His study on IBS patients also showed that inclusion of anxiety and depression together as covariates removed the group differences in the left pregenual ACC. A recent metaanalysis indicated that gray matter reduction in the ACC was the most consistent finding in VBM studies of major depressive disorder. The present results indicated that although the ACC is involved in multiple functions, such as the gastrointestinal signal process and emotional and cognitive controls, the anatomic alterations in the ACC in the meal-related FD patients were more likely to be associated with emotional changes and could be attributed neither to the durations nor to the symptoms. In summary, this study demonstrated the cerebral morphometric alterations in the meal-related FD patient and the influence of psychological factors on the regional brain structure. Although the majority of the structure-changed regions were related to emotional and cognitive processes, psychosocial dysfunction could not fully explain the microstructural alterations. The cerebral microstructural changes in the meal-related FD patients might be induced by multiple factors, including abnormal sensory input and psychosocial dysfunction, etc.Is HE4 secreted by ovarian cancer patients in the highly glycosylated form? Is there a heteroplasmon of HE4 like AFP-L3? Can Lewis y antigen be effectively utilized as a specific marker for monitoring the disease? These issues remain to be resolved.Our preliminary data indicated that Lewis y antigen is a component of HE4, and both are expressed at high levels in ovarian cancer, which was further confirmed using correlation analysis. Lewis y antigen of HE4 may thus contribute to changes in specific biological behaviors, including adhesion and migration of ovarian carcinoma cells, via the corresponding signal transduction pathways. However, the specific mechanisms underlying the activities of HE4 and Lewis y antigen in ovarian cancer development are currently unclear. To explain the occurrence and development of ovarian cancer, and aid in clinical diagnosis and assessment.
Hepatic artery chemotherapeutic infusion defined as injection of evidence of a difference in effectiveness
This method for the construction of cRNA standards was simple and is suitable to measure transcripts of any genes of interest. Recently, qRT-PCR assays based on the TaqMan probes have been developed for the detection of hantaviruses in rodents, cell culture or HFRS patients. In this study, a SYBR Green based one-step qRT-PCR assay coupled with melting curve analysis was established to quantify the HTNV RNA viral load. This method is highly specific and sensitive compared to conventional RT-PCR. It is also a high-throughput method for the detection and quantification of HTNV in clinical studies. The entire course of viral RNA extraction and qRTPCR test consumed approximately three hours, making it a fast and simple assay. Due to the limitation of numbers of HFRS AbMole Metyrapone patients in the study, the clinical performance of the assay must be further evaluated. Additionally, the relationship between the HTNV RNA viral load and the severity of the disease must be analyzed, and the association of the dynamic changes in HTNV RNA copy numbers in the serum samples of HFRS patients with disease development must be monitored. The quest for high quality, yet sustainable dementia care is becoming ever more challenging. Dementia is an important and in numbers growing cause of disability and burden of care and one of the diseases with the largest per capita healthcare consumption. Moreover, there is a strong trend towards early diagnosis in dementia, which may increase the period during which care for patients with dementia will be asked for. These developments urge to answer the questions of how to optimise care for this population and how to ensure this care for future generations. Trying to answer these questions, several countries have developed national dementia strategies. Many of these strategies focus on the nationwide availability of memory clinics. Therefore, the number of memory clinics in different countries increased rapidly over the last decades. Memory clinics used to focus on diagnosing patients with dementia. Today, memory clinics are also increasingly involved in post-diagnosis treatment and care co-ordination of patients with dementia. There are data supporting the cost-effectiveness of memory clinics as a diagnostic setting. However, evidence about memory clinics being cost-effective in post-diagnosis treatment of dementia and follow-up care is scarce. Knapp and colleagues reviewed the literature on economic evaluations of dementia care. They found that the majority of the economic evidence was on pharmacological interventions. The non-pharmacological interventions, on which they found AbMole Etidronate little economic evidence was often of poor quality and harder to interpret.
Chondrocyte metabolism with respect to collagen and GAG synthesis in vivo
The reinforces possibility satisfactory therapy await discovery fundamental proximal pathogenesis effects of LOX on other cells may need to be elucidated prior to conducting animal studies with this enzyme. A similar process would allow the identification of an optimal LOX concentration for maximizing the native-to-native integration strength; this will be immensely useful from a  clinical perspective, once the safety and efficacy of exogenous LOX has been shown. While other cross-linkers such as ribose, glutaraldehyde, genipin, and methylglyoxal have all been investigated in conjunction with engineered articular cartilage, these agents have all been shown to alter cellular activity. Some of these agents are even cytotoxic and thus preclude their use with live cells in influencing integration. Furthermore, unnatural cross-linkers such as glutaraldehyde have been shown to elicit a foreign body giant cell reaction, in contrast to LOX, which is found naturally in multiple musculoskeletal tissues. This study demonstrates that LOX is a potent agent for enhancing integration between native and tissue engineered cartilage. It also paves the way for the use of LOX in improving native cartilage integration. These results could potentially be used to solve the problem of large cartilage defects by allowing tissue engineered cartilage implants to be integrated into the surrounding tissue. The multifunctional mannose 6 phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor, hereafter referred to as IGF2R, mediates endocytosis and subsequent clearance or activation of a variety of ligands involved in the regulation of cell growth and motility, including insulin-like growth factor 2 and transforming growth factor b. The IGF2R gene shows developmental stage specific expression levels which are highest in the fetus and decline rapidly after birth. Murine Igf2r is imprinted and switches from biallelic to maternal expression during implantation. By the fetal stage, expression from the maternal allele is established in all tissues of the conceptus with the exception of brain, which escapes imprinting. In contrast, imprinting of IGF2R in human remains controversial, with exclusive biallelic expression, maternal or biallelic expression and partial imprinting reported for fetal and/or placental samples. The fundamental role of Igf2r in prenatal growth regulation suggests that quantitative variation in imprinting could affect phenotype via gene dosage effects. Indirect evidence for such an effect was obtained in the sheep model where fetal overgrowth induced by embryo culture was associated with hypomethylation at a CpG site in an intronic sequence element implicated in IGF2R imprinting and down regulated IGF2R expression. However, the imprinting status of IGF2R was not determined in this study. Species differences in imprinting, in particular in the placenta, appear to be linked to differences in reproductive strategies, e.g. litter size, gestational length, maturity of newborns and lifetime reproductive capability. The inconsistent data on IGF2R imprinting in human have been interpreted as evidence for a polymorphic trait, where the observed minority of imprinted or partially imprinted specimens could signal an evolutionary transition to biallelic expression in the population. It was further hypothesized that differences in imprinting of Igf2r/IGF2R between mouse and human could be a consequence of different reproductive strategies, including competition between multiple fetuses and the shorter gestation period requiring a more efficient placenta in mouse. However, comparative data from other species suitable for testing this hypothesis are lacking. The domestic cow has a similar gestation length as human, carries a single conceptus with comparable maturity at birth, has a similar lifetime reproductive capability, and shows a conserved IGF2R gene structure with high sequence homology to human.
clinical perspective, once the safety and efficacy of exogenous LOX has been shown. While other cross-linkers such as ribose, glutaraldehyde, genipin, and methylglyoxal have all been investigated in conjunction with engineered articular cartilage, these agents have all been shown to alter cellular activity. Some of these agents are even cytotoxic and thus preclude their use with live cells in influencing integration. Furthermore, unnatural cross-linkers such as glutaraldehyde have been shown to elicit a foreign body giant cell reaction, in contrast to LOX, which is found naturally in multiple musculoskeletal tissues. This study demonstrates that LOX is a potent agent for enhancing integration between native and tissue engineered cartilage. It also paves the way for the use of LOX in improving native cartilage integration. These results could potentially be used to solve the problem of large cartilage defects by allowing tissue engineered cartilage implants to be integrated into the surrounding tissue. The multifunctional mannose 6 phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor, hereafter referred to as IGF2R, mediates endocytosis and subsequent clearance or activation of a variety of ligands involved in the regulation of cell growth and motility, including insulin-like growth factor 2 and transforming growth factor b. The IGF2R gene shows developmental stage specific expression levels which are highest in the fetus and decline rapidly after birth. Murine Igf2r is imprinted and switches from biallelic to maternal expression during implantation. By the fetal stage, expression from the maternal allele is established in all tissues of the conceptus with the exception of brain, which escapes imprinting. In contrast, imprinting of IGF2R in human remains controversial, with exclusive biallelic expression, maternal or biallelic expression and partial imprinting reported for fetal and/or placental samples. The fundamental role of Igf2r in prenatal growth regulation suggests that quantitative variation in imprinting could affect phenotype via gene dosage effects. Indirect evidence for such an effect was obtained in the sheep model where fetal overgrowth induced by embryo culture was associated with hypomethylation at a CpG site in an intronic sequence element implicated in IGF2R imprinting and down regulated IGF2R expression. However, the imprinting status of IGF2R was not determined in this study. Species differences in imprinting, in particular in the placenta, appear to be linked to differences in reproductive strategies, e.g. litter size, gestational length, maturity of newborns and lifetime reproductive capability. The inconsistent data on IGF2R imprinting in human have been interpreted as evidence for a polymorphic trait, where the observed minority of imprinted or partially imprinted specimens could signal an evolutionary transition to biallelic expression in the population. It was further hypothesized that differences in imprinting of Igf2r/IGF2R between mouse and human could be a consequence of different reproductive strategies, including competition between multiple fetuses and the shorter gestation period requiring a more efficient placenta in mouse. However, comparative data from other species suitable for testing this hypothesis are lacking. The domestic cow has a similar gestation length as human, carries a single conceptus with comparable maturity at birth, has a similar lifetime reproductive capability, and shows a conserved IGF2R gene structure with high sequence homology to human.