Tumor microenvironment is a dominant force in inducing resistance to therapy in multiple malignancies. Tumor microenvironment plays a key role in leukemic stem cell maintenance and in modulating signal transduction and resistance in CML and AML. In conclusion, the combination of bortezomib and mitotic inhibitors such as paclitaxel, docetaxel, vincristine or BI 2536 is an effective strategy for targeting of both TKIs -resistant and sensitive Bcr-Abl-positive leukemic cells. These regimens are able to inhibit Bcr-Abl activity and its downstream signaling, and to activate caspase-dependent cell death. In addition, these regimens are able to overcome the resistance to imatinib, dasatinib and nilotinib, brought about by Bcr-Abl protein overexpression or Bcr-Abl mutations, making them attractive potential therapies for Bcr-Abl-positive leukemias such as CML, especially for those resistant to current treatments. As the combined treatment is also efficient in non-CML Bcr-Abl positive cells such as the Baf3 Bcr-Abl cell line, it may also be a promising therapy for non-CML Ph+ leukemias. The initiation of DNA replication is temporally divided into two phases during the cell cycle. First, an inactive form of the replicative MCM helicase is loaded onto origin DNA in G1 phase and then activated upon entry into and during S phase by two sets of kinases: cyclindependent kinase and Dbf4-dependent kinase. DDK is a two-subunit Ser/Thr kinase composed of the Cdc7 kinase and Dbf4 regulatory subunits. DDK mediated phosphorylation of the six-subunit Mcm2-7 helicase is thought to bring about a conformational change in its structure leading to helicase activation. MCM activation is followed by localized DNA unwinding, recruitment of the replisome machinery and the initiation of bi-directional DNA synthesis. Other functions of DDK include facilitation of chromosomal segregation in mitosis and meiosis, the initiation of meiotic recombination, and activation of DNA R428 repair pathways including trans-lesion DNA repair. Cdc7 kinase activity depends on association with its regulatory subunit, Dbf4. Dbf4 is a cell cycle regulated protein whose Ibrutinib Src-bcr-Abl inhibitor abundance peaks during S-phase and then is degraded by end of mitosis. Interaction with Dbf4 is necessary for Cdc7 ATP binding and substrate recognition. Like all protein kinases, the DDK crystal structure reveals an active site in a deep cleft between the N- and C-terminal lobes. The Dbf4 Zn-finger binds to the N-terminal lobe of DDK and is necessary for human DDK activity but is not essential for budding or fission yeast DDK kinase activity. Dbf4 motif M enhances its association with the Cdc7 subunit and is required for the full activity of the kinase in yeast and humans. DDK phosphorylates multiple subunits of the MCM helicase and a recent study in budding yeast indicates that Cdc7 and Dbf4 physically interact with distinct subunits of the Mcm2-7 complex. DDK is over expressed in a number of primary tumors and tumor cell lines. DDK over expression has also been associated with poor prognosis in breast cancers, advanced clinical stage in ovarian carcinoma, and with aggressive phenotype in papillary thyroid carcinomas. Regulating the levels of DDK in tumor cells is an attractive tumor therapeutic strategy. Using neutralizing antibodies, Hunter and colleagues were the first to show that DDK depletion leads to severe disruption of DNA replication in HeLa cells. Using small interfering 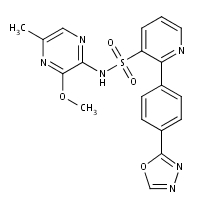 RNAs, Santocanale and colleagues further showed that DDK depletion led to p53-independent apoptosis in HeLa cells whereas a normal human dermal fibroblast cell line underwent a reversible cell-cycle arrest. HeLa cells were unable to arrest at the G1-S phase transition, progressing through a lethal S phase resulting in cell death via apoptosis. This finding has been corroborated in a number of different cell lines. Importantly, tumor cell death induced by depletion of DDK is not accompanied by the induction of known checkpoint markers.
RNAs, Santocanale and colleagues further showed that DDK depletion led to p53-independent apoptosis in HeLa cells whereas a normal human dermal fibroblast cell line underwent a reversible cell-cycle arrest. HeLa cells were unable to arrest at the G1-S phase transition, progressing through a lethal S phase resulting in cell death via apoptosis. This finding has been corroborated in a number of different cell lines. Importantly, tumor cell death induced by depletion of DDK is not accompanied by the induction of known checkpoint markers.